Chemical vapour deposition or CVD is a name for a group of processes, which involve depositing a solid material from a gaseous phase. It is similar in some respects to physical vapour deposition (PVD). In PVD precursors are solids. Which are evaporated and deposited onto substrates.
Types of CVD processes.
- Atmospheric pressure chemical vapour deposition (APCVD)
- Low pressure chemical vapour deposition (LPCVD)
- Metal-Organic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD)
- Plasma assisted chemical vapour deposition (PACVD)
- Plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD)
- Laser chemical vapour deposition (LCVD)
- Photo chemical vapour deposition (PCVD)
- Chemical vapour infiltration (CVI)
- Chemical beam epitaxy (CBE)
CVD Process:
In this process, carrier gases and precursor gases are added to reaction chamber at ambient temperature. As they come into contact with heated substrate, they react forming solid phases and deposited onto substrate. In this process substrate temperature is important to achieve desired results. Coatings produced by CVD are fine grained and also are of high purity. CVD process deposition rate is very slow and also these coatings are only few microns thin.
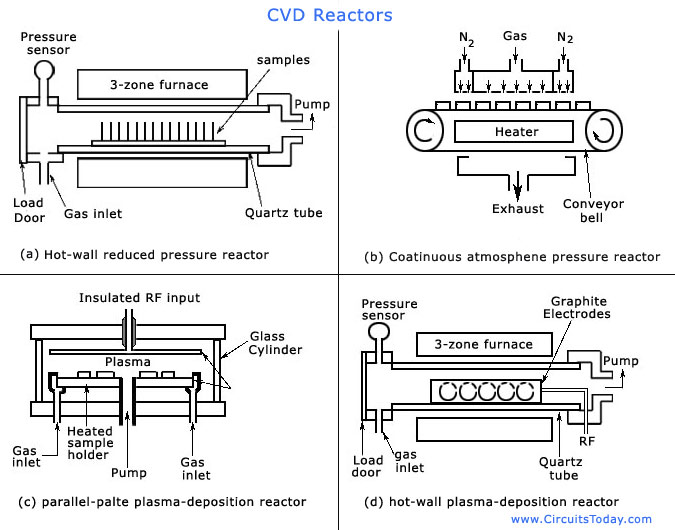
CVD Equipment
Equipment consists of several components:
Gas delivery system for supplying gases and precursors to reaction chamber
Reaction chamber – deposition takes place inside the chamber
Substrate loading and removing mechanism
Energy source which provides the heat for reaction.
Vacuum system for removing gases other than those required for the reaction.
Exhaust system to remove volatile products from the reaction chamber. In some cases exhaust gases maybe not suitable to release into the atmosphere therefore a system may require for treatment to make them safe to release.
Process control equipments like gauges, controls etc to monitor process parameters such as pressure, temperature and time.
Energy sources
Below are the sources of heat for CVD process.
- Resistance heating
- Radiant heating
- Induction heating
Other energy sources can be like UV light and lasers.
Precursors
In CVD process, materials are deposited from the gaseous state and therefore precursors for CVD processes must be volatile. Also, they must be stable enough to be delivered to the reaction chamber.
Precursor will only deposit a single element to the substrate material whereas volatile matter will get evaporated in the process. However sometimes precursors may provide more than one element. Such materials simplify the delivery system because they reduce the number of reactants required to produce a given compound.
Precursor Materials
These materials are Halides, Hydrides, Metal Organic Compounds, Metal Alkyls, Metal Alkoxides, Metal Di-alkylamides, Metal Diketones, Metal Carbonyls and others include a range of other metal organic compounds. also complexes and ligands.
Materials produced by CVD process
CVD is used to process almost any metallic or ceramic compound like metals and alloys, carbide, nitride, boride and also oxides.
Applications
CVD has wide range of applications in different industries such as:
- Coatings – Coatings for a variety of applications like wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature protection, erosion protection and also their combinations.
- Semiconductors and related devices – Integrated circuits, sensors and also optoelectronic devices
- Dense structural parts – CVD can be used to produce components which are difficult and also uneconomical to produce using conventional fabrication techniques. Dense parts produced via CVD are generally thin walled and maybe deposited onto a mandrel or former.
- Optical Fibers – For telecommunications.
- Composites – Preforms can be infiltrated using CVD techniques to produce ceramic matrix composites such as carbon-carbon, carbon-silicon carbide and silicon carbide-silicon carbide composites. This process is sometimes called chemical vapour infiltration or CVI.
- Powder production – Production of nano powders and fibers
For more articles in Vacuum Technology please subscribe
