Carbon
Carbon occurs in different forms. For example, diamond, graphite, carbon nano-tubes, fullerene and graphene with different bonding and structures. Same carbon cab be used to make synthetic diamonds by chemical vapour deposition process.
Graphite and diamond are most common forms of carbon and on the other hand graphene is recent development with new applications.
The structure and bonding between the carbon atoms gives different properties to these elements.
For example, graphite is soft and diamond is hardest natural material. On the other hand graphene occurs in single sheets and has unique properties.
Synthesis
There are two methods to produce diamond as thin film, one is HPHT and another is CVD. HPHT is very old method but CVD is the latest technology to produce different types of thin films and diamond wafers.

If we heat carbon under pressure, as a result it can form diamond. This is the reason in early stages of diamond synthesis High Temperature and High Pressure (HTHP) process was developed.
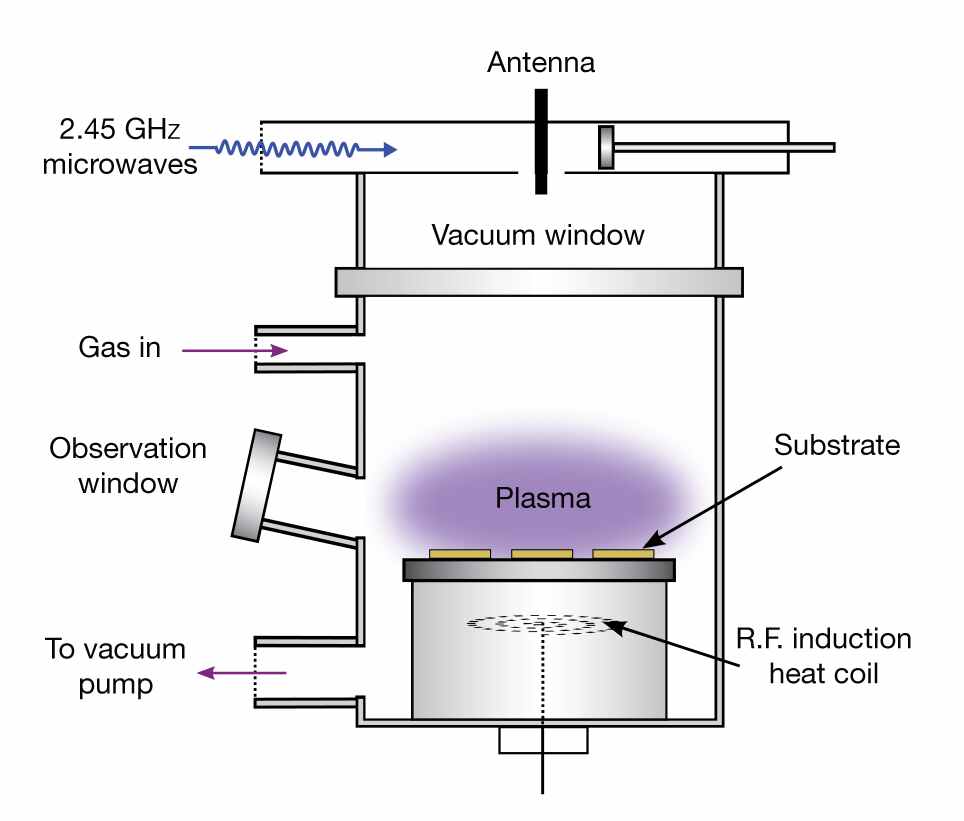
HTHP process has three main limitations. Firstly, a very high temperature to convert graphite to diamond. Secondly, it needs extreme pressure. Finally, if you get diamond, the grains are very small.
These are the reasons why CVD process came into picture. The most common example of CVD process is pyrolytic carbon. Formation of soot during the burning of fire wood because of incomplete oxidation.
Types of CVD process
There are many different types of CVD process to achieve high rate of diamond synthesis.
- Plasma Enhanced CVD
- Micro wave – Plasma Enhanced CVD
- RF Plasma Enhanced CVD
- DC Plasma Enhanced CVD
- Hot Filament CVD
Substrates for growing diamond
Properties
There are three main properties the substrate must have and are as below.
- Melting point of substrate must be higher than deposition temperature.
- Substrate should form carbide layer onto which it can adhere and deposit.
- Substrate should have similar thermal expansion coefficient to diamond in order to prevent film cracking during growth.
The metals such as gold, silver, lead, tin and copper as well as non-metals like germanium, diamond itself, graphite and sapphire are not suitable for diamond growth. These metals and non-metals do not form carbide layer to support diamond film. These can be used in case of growing free-standing diamond films because of no adherence of film it is easier to remove the film.
There are metals like pt, pd, Rh, Fe, Ni, and Ti with high carbon solubility. They absorb carbon like sink. The growth of diamond starts after carbon saturates the substrate. In some materials like TI carbide layer continues to grow during diamond deposition. This affects the mechanical properties of the object and limits its applications.
Some common non- metals such as Si, B, SiO2 and Si3N4 form limited carbide layer onto which diamond can be deposited. Carbide substrates like SiC, WC, and TiC are common for diamond deposition. One of the most used substrates for diamond deposition is silicon. It has all the characteristics like high melting point. It also forms required carbide layer and has low thermal expansion coefficient. Tungsten and Molybdenum has similar properties like Silicon. They are also very popular substrates in diamond deposition.
Applications of Diamond
Synthetic Diamond has unique chemical, thermal and mechanical properties which makes it suitable for application in cutting tools. Three most important properties of diamond make it suitable for this application and they are high thermal conductivity, extreme hardness and also low coefficient of friction.

Diamond thin films are also suitable as protective coatings for cutting tools and metal working industry.
Different CVD methods are used to produce diamond coating on complex shapes of tools.
High optical band gap makes synthetic diamond materials suitable for optical applications. It is also radiation resistant and hence it is also used in optical windows in space applications.
Its chemical inertness also makes it suitable for biomedical implants.
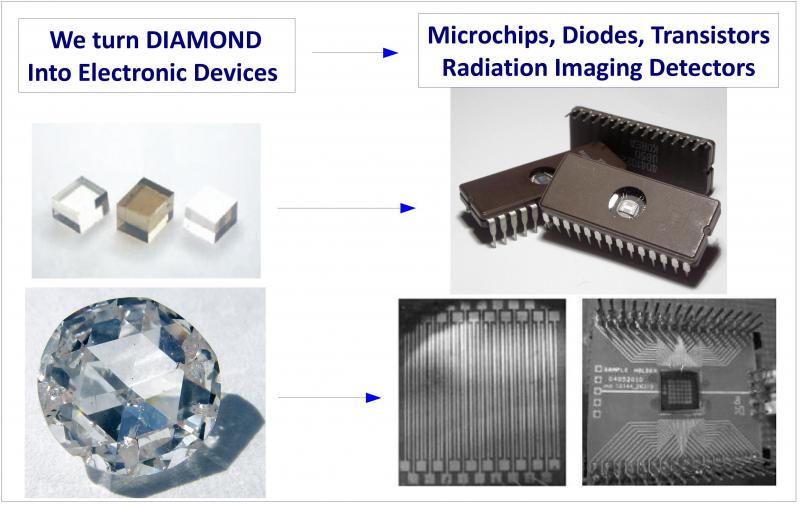
Its properties also make it suitable for many electronics applications and technologies used in multi-chip manufacturing.
For More articles on Vacuum Technology please subscribe
