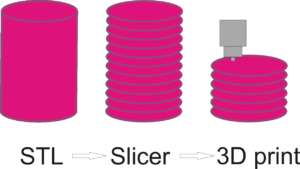
3D printers need to convert the 3D models into printable file format. A slicing software can do this job. It converts the STL file into layered structure. The 3D printer slicer or slicing software converts 3D model in STL format into G code format.
The slicer first converts object into stack of layers followed by other specifications like infills, supports, base layers, print speed and temperature are converted to G-code. this file prints the 3d model.
Features of Slicer Software
- Infill
- Infill pattern
- Support Structure
- Base Layers (Rafts, Skirts and Brims)
- Object orientation
- Layer height or resolution
- Object Shell Thickness
- Print Speed
- Print path
- Temperature
- Number of Extruders
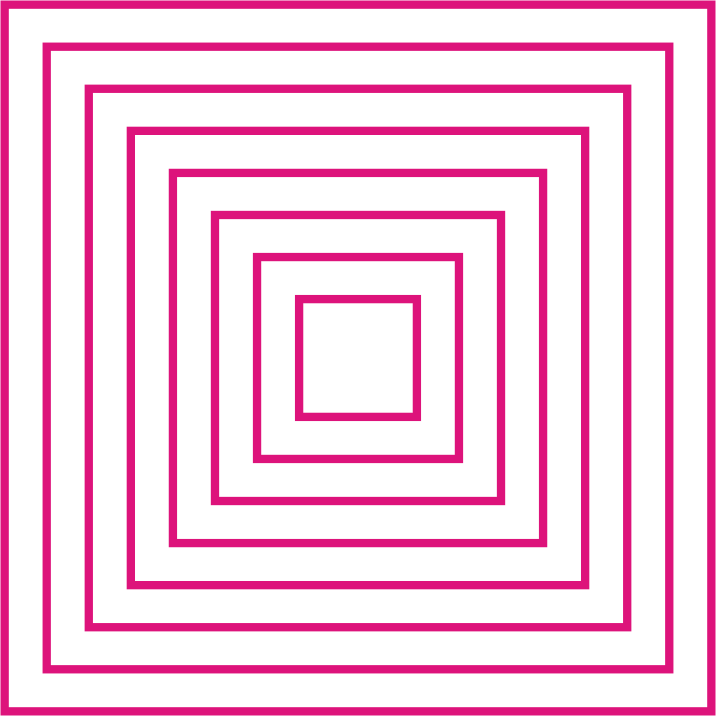
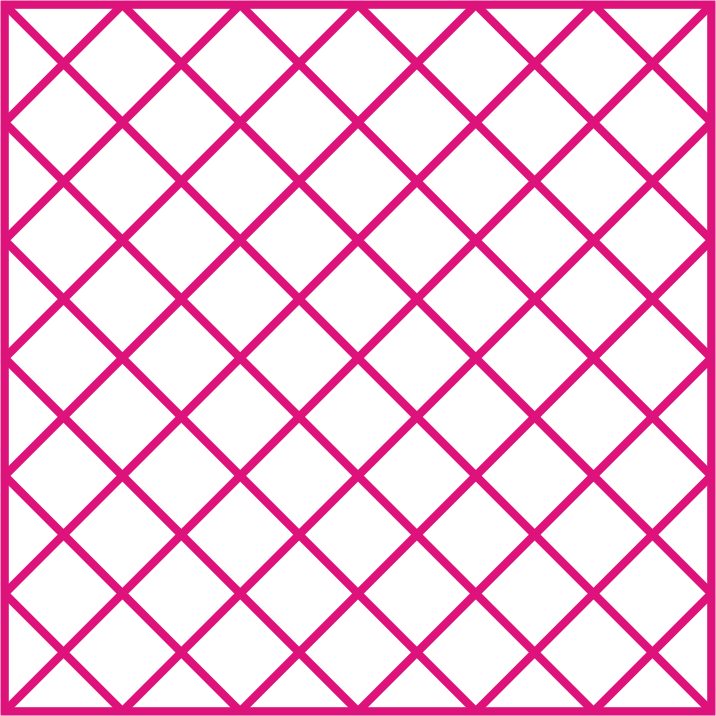
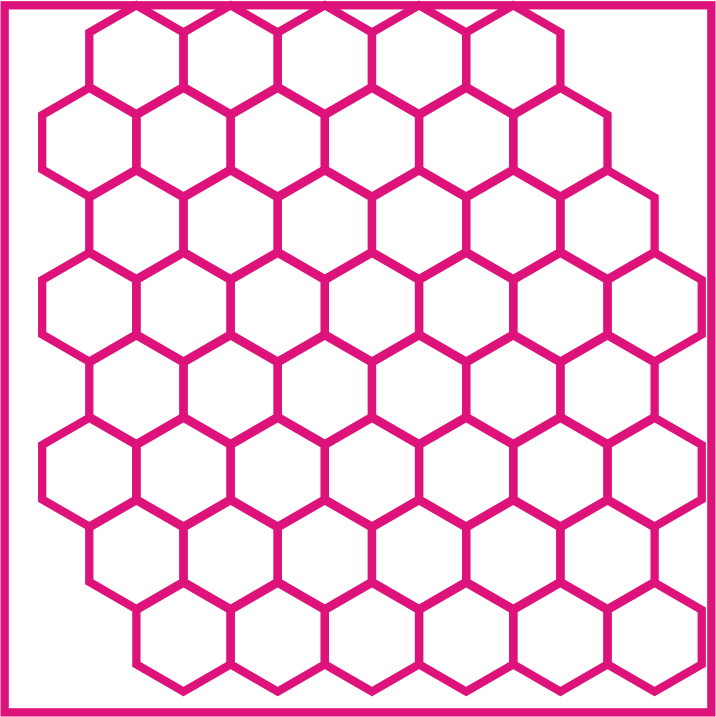
Infill & Infill Pattern
3D objects or models are solid and it takes large amount of material and print time. This increase the cost of printing. The slicer converts this solid object into hollow and adds internal structure of walls to provide strength.
Infill density is the amount of internal structure in a object. The 3D Printing Slicing software helps to set infill density as well as type of infill pattern. The design of the infill pattern can have an impact on the strength and flexibility of the 3D prints
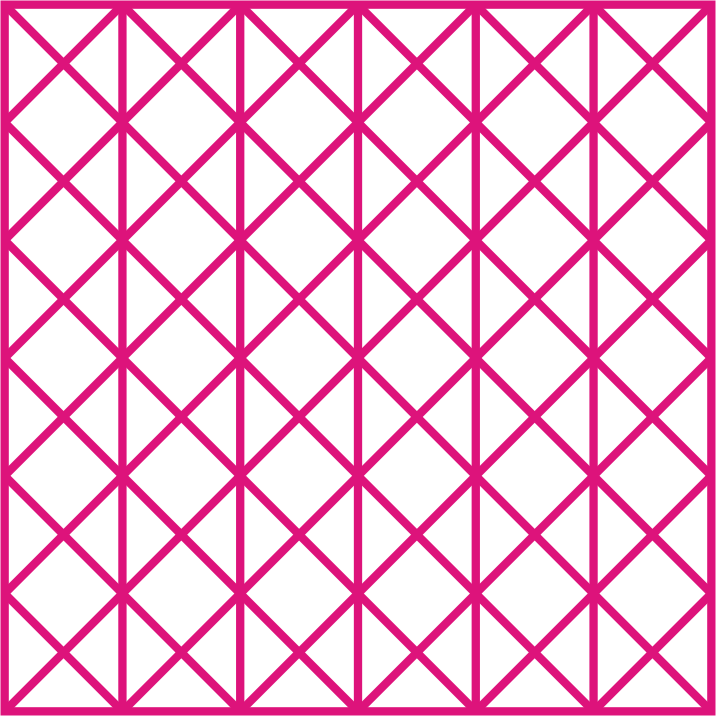
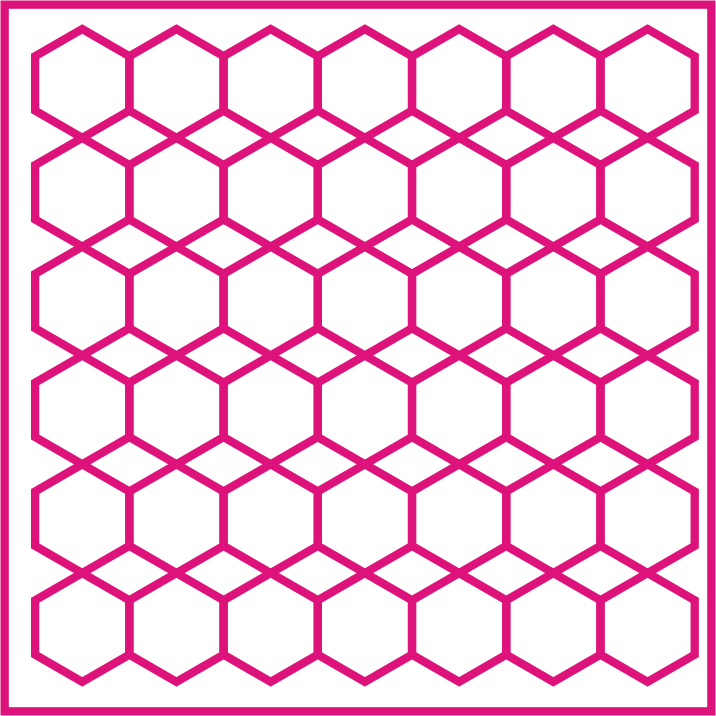
Support Structure
Printer prints, one layer on another existing layer. This means every layer needs an underlying layer to support it. If a model has an overhanging part, it still needs a supporting layer. This supporting layer is called the support structure.
Overhangs less than 45 degrees in angle and bridges more than 20mm long needs supports. These are examples of where models need support.
Base Layers (Rafts, Skirts and Brims)
3d printed objects get stuck to the printer bed and also generate variations in printed object. This is because of the printer bed properties. The slicer provides base layers like rafts, skirts and brims to avoid these problems. Skirt is a single outline layer printed around the base of the object and not touching its base. The Brim layer is the first print layer which touches the base of the object, lastly raft is the base layer under the bottom of the object.
Object Orientation
We need to align the 3d printing model in the given space. 3d printer volume and part size are main points which decides orientation.
Layer Height or Resolution
Different layer height generates different resolution. Smaller layer height gives high resolution and smooth surfaces. It takes more time to print with high resolution and smooth surface objects.


Object Shell Thickness
Outer Shell Thickness is the outer layer thickness of the 3D object. The strength of the object is dependent on the number of shells present. Higher shell count results in higher strength.
Print Speed
The 3D Slicer software has default speed setting. These settings can be changed based on the geometry of the object. The speed can also vary depending on the material used for printing. Every slicer software has print speed parameters which should be considered based on 3D object.
Print Path
Printing paths have direct impact on printing time, surface roughness and strength of the model. Therefore it is the printing path is crucial in 3D printing. A path planning strategy can help optimize the overall printing process. This will result in a shorter fabrication time. Every slicing program for 3d printing has built in printer paths.

Temperature in slicer software
Printer temperature is related to printer speed. If printer speed is set to higher then printer temperature should be increased. if the print speed is not matched to the temperature, it can lead to “under extrusion” due to improper melting of filaments. Also, high temperatures can lead to “over extrusion” and result in blobs or zits.
lastly, printer temperature also depends on material type. Different polymers have different requirements of nozzle and print bed tempertaures.
Number of Extruders
If you have multiple extruders on the machine, 3D slicer program helps to assign different roles to each extruder. Nowadays, many printers come with multiple extruders. These can print materials with different colors and different properties.
List of 3d Printer Slicer Software
There is a wide range of free 3D slicer software available, some of them are free and opensource.
| Software | User | Price | OS |
|---|---|---|---|
| PrusaSlicer | Beginners, Advanced Users | Free | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| Outpoint | Intermediate Users, Advanced Users | Free | Raspberry Pi, Windows, Mac Linux |
| Slic3r | Advanced Users, Professional Users | Free | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| IceSL | Advanced Users | Free | Windows, Linux |
| MatterControl | Beginners, Advanced Users | Free | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| Repetier | Intermediate Users, Advanced Users | Free | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| ideaMaker | Beginners, Advanced Users | Free | Windows, Mac, Linux |
| Z-SUITE | Beginners | Free | Windows, Mac |
| MakerBot Print | Beginners | Free | Windows, Mac |
| Tinkerine Cloud | Beginners | Free | Browser |
| SuperSlicer | Intermediate Users, Advanced Users | Free | Windows, MacOS, Linux |
| Astroprint | Intermediate Users | Free | Raspberry Pi and pcDuino systems |
| Pathio | No data | Free | No data |
| Craftware | Beginner | Free | Windows, Mac |
| Kiri:Moto | Beginner | Free | Browser |
